@中国诗情感分析Sentiment Analysis on Classical Chinese Poetry
本篇论文旨在提高对古典诗歌情感分析的性能,并通过引入增强层次注意力和短行情感标签的多任务框架来实现这一目标。该方法利用了组成诗歌的独特信息,并将情感分析应用于整体诗歌和短行。实验结果表明,该方法优于现有技术,在准确性和F1 宏得分方面均取得了显著提升。
we propose to utilize the unique information from the individual short lines that compose the poem, and introduce a multi-task framework with hierarchical attention enhanced with short line sentiment labels.
介绍
To analyse sentiment in classical Chinese po-etry, previous studies have explored different methods, for example, constructing sentiment lexicons(Hou and Frank, 2015; Zhang et al., 2023), transferring knowledge from modern Chinese(Zhao et al., 2014), or extracting imagery words(Shen et al., 2019; Su et al., 2023). 【现有的情感分析方法:构建情感词典,从现代汉语翻译中转移知识,抽取意象词】
Although these studies improved the general performance for the task of sentiment analysis in classical Chinese poetry, by utilizing special words in the poems or draw-ing upon knowledge beyond the poems, they did not consider the compositional structure of the po-ems. (没有考虑诗歌的成分结构)Usually, a classical Chinese poem comprises several short lines, which may show different emo-tions, and in return, contribute to the overall emo-tion expression of the poem. (短句可能有不同的情感)Thus in this paper, for the task of sentiment analysis of classical Chinese poetry, we propose to take the sentiment of short lines into consideration by using a multi-task framework with a hierarchical attention network, which includes the sentiment analysis task of both the overall poem and the short lines of which the poem is comprised. We will show that, by leveraging the sentiment information from the short lines, we can outperform the current state-of-the-art in sentiment analysis of ancient Chinese poetry.
F1值细分类
相关工作
1. 通用诗歌情感分析方法
- 基础方法:
- 使用情感词典分析诗歌情感(Kao & Jurafsky, 2012)
- SPARSAR系统结合句法、语义和韵律分析(Delmonte et al., 2013)
- 机器学习与深度学习:
- 基于CNN的泰语诗歌分类(Promrit & Waijanya, 2017)
- 注意力机制模型(如C-BiLSTM)用于诗歌情感分类(Ahmad et al., 2020b)
- 多语言研究:涵盖拉丁语(Sprugnoli et al., 2022)、旁遮普语(Kaur & Saini, 2020)等
2. 古典中文诗歌的专项研究
- 技术方法:
- 情感词典构建:基于图模型(Hou & Frank, 2015)或结合监督学习(Zhang et al., 2023)
- tfidf (Li and Li2018)
- 字符和单词层面的情感意象(Shen et al., 2019)
- 视觉模态信息(Su et al., 2023)
- 知识迁移:利用现代汉语翻译辅助分析(Zhao et al., 2014)
- 预训练模型:AnchiBERT(Tian et al., 2021)、SikuBERT(Wang et al., 2022)等针对古汉语优化
3. 多任务学习与分层注意力机制
- 多任务框架:
- 联合学习粗/细粒度情感任务(Balikas et al., 2017)
- 结合方面提取与情感分类(He et al., 2019)
- 分层注意力网络(HAN):
- 文档级分类(Yang et al., 2016)及社交媒体分析(Cheng et al., 2019)
- 在电子学习文本情感分类(Chanaa et al., 2021)等领域的应用
Aspect-based sentiment analysis(ABSA,基于方面的情感分析)是一种细粒度的情感分析任务,旨在识别句子中针对特定方面(Aspect)的情感极性。
Hierarchical Attention Network(HAN,层级注意力网络)是一种面向长文本(如文档、篇章)分类的深度学习模型,由Zichao Yang等人在2016年提出。其核心思想是通过模仿人类阅读文档时的层次化注意力机制,捕捉不同层次的文本重要性差异。
数据集
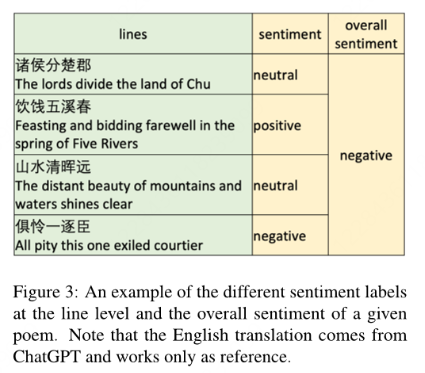
Thanks to the work of Chen et al. (2019), we now have a fine-grained sentimental poetry corpus (FSPC), which we are going to utilize in our experiments.
方法
- 数据预处理
- 特征提取和微调
- 特征提取
- 用预训练模型生成向量表示
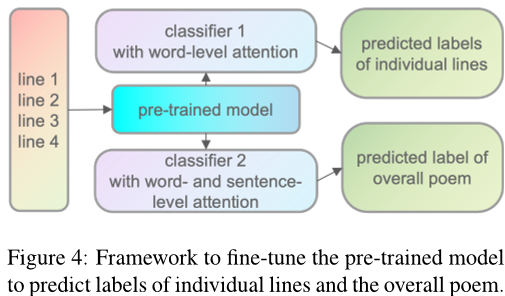
- 微调:多任务学习架构:
- 任务1(短句情感分类):在预训练模型顶部添加线性分类层,预测每个短句的情感标签(Negative/Neutral/Positive)。
- 任务2(整体诗歌情感分类):在另一分支中,通过分层注意力网络(HAN)融合词级和句子级特征,预测诗歌整体情感。
- 参数共享:两个任务共享预训练模型参数,通过反向传播联合优化。
- 特征提取
- 增强句子级别的注意力 additional in-formation derived from the line labels is integrated into the sentence-level attention scores.
- 结果评估:accuracy and F1-macro
实验及结果
1. 实验设计
-
数据集:基于 FSPC(5,000首古典诗歌,含诗级和行级情感标签),合并隐性情感为三分类(Negative/Neutral/Positive)。
-
评估方法:
- 十折交叉验证:避免数据划分偏差,结果取10次平均。
- 指标:Accuracy(准确率)和F1-macro(类别均衡评估)。
- 对比基准:现有研究(Zhang et al., 2022; Hong et al., 2023)的最佳结果(F1 64.8%)。
-
实验分两组:
- 实验1:基于SikuBERT,对比不同框架复杂度(单任务、多任务、多任务+HAN、多任务+HAN+短句标签增强)。
- 实验2:在最佳框架下,对比不同预训练模型(BERT-base-Chinese、BERT-ancient-Chinese、SikuBERT、SikuRoBERTa等)。
2. 关键结果
实验1:框架复杂度影响
| 模型配置 | Accuracy (%) | F1-macro (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 单任务(仅整体情感分类) | 69.00 | 66.27 |
| 多任务(联合短句+整体分类) | 69.32 | 66.50 |
| 多任务 + HAN | 70.06 | 67.49 |
| 多任务 + HAN + 短句标签增强 | 70.96 | 68.51 |
- 结论:
- 多任务学习(+0.23% F1)和分层注意力(+1.99% F1)均带来显著提升。
- 短句标签增强进一步优化注意力权重,证明结构化信息利用的有效性。
实验2:预训练模型对比
| 预训练模型 | Accuracy (%) | F1-macro (%) |
|---|---|---|
| BERT_CCPoem | 67.54 | 65.24 |
| BERT-base-Chinese | 69.60 | 67.33 |
| BERT-ancient-Chinese | 70.28 | 68.31 |
| SikuBERT | 70.96 | 68.51 |
| SikuRoBERTa | 72.88 | 71.05 |
- 结论:
- 古汉语优化模型(SikuRoBERTa)性能最佳,F1比现代汉语模型(BERT-base)高3.72%。
- 专用于诗歌的BERT_CCPoem表现不佳,可能因训练数据局限(仅诗歌语料)。
3. 结果分析
- 类别差异:
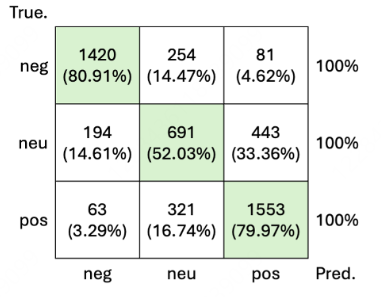
- 负面/正面诗歌:模型准确率约80%(情感表达明确)。
- 中性诗歌:准确率仅52.03%,因隐含情感难以捕捉
- 从十折交叉验证的预测结果中,提取所有真实标签为中性但被模型预测为负面或正面的诗歌。
- 统计数量:
- 中性→负面:194首(占中性错误预测的约1/3)
- 中性→正面:443首(占中性错误预测的约2/3)
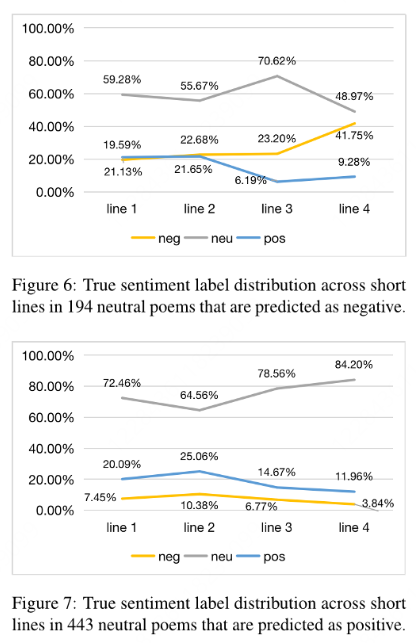
- 按行位置分组
- 将每组诗歌的短句按行位置(第1行、第2行、第3行、第4行)归类,形成四个独立的数据子集。
4. 性能突破
- SOTA对比:
- 本文最佳模型(SikuRoBERTa+HAN+短句增强)F1达71.05%,较之前最优(Hong et al., 2023)提升6.25%。
- 证明多任务框架与结构化注意力在古典诗歌分析中的有效性。